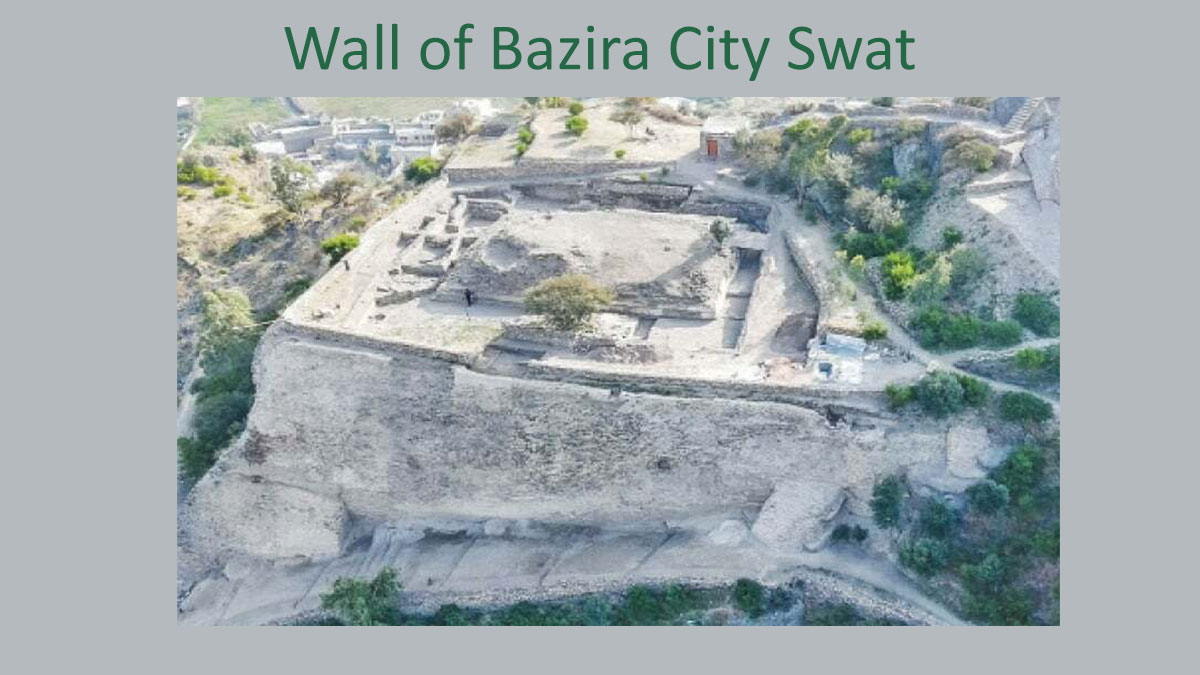
International archaeologists and conservationists said that the north-eastern fortification wall of Bazira city, which is of great importance to the Gandhara region, would be completely conserved using scientific techniques by next year.
The international alliance for the protection of heritage in conflict areas (Aliph) launched the “Saving the archaeological site of Bazira” conservation project in April 2022 in collaboration with the International Association for Mediterranean and Oriental Studies (ISMEO) and the provincial department of archaeology and museums.
The project will prioritise the preservation of the acropolis as well as the establishment of a buffer zone and archaeological park on Ghwandai top in Bazira city.
The activity is led by Fabio Colombo, an internationally recognised restoration and conservation expert who has been a member of the ISMEO Italian Mission since 2011. He also finished restoring the Jahanabad Buddha after militants defaced it in 2007. The project also includes renowned conservation expert Marco Pinelli from Accademia di Brera in Milan, Italy, who has been working with ISMEO Italian Mission since 2019.
The conservation of the fortification wall began in April 2022, according to Marco Pinelli, who is currently working on it. “At first, the wall was in a dilapidated state. It was overgrown with vegetation, and the majority of the stones were loose and falling down, making it fragile and on the verge of collapsing,” he added.
Read More: 400-year-old tunnel discovered in Shahi Qila
He stated that they initially began conservation work on the north side of the Kushan-era retaining wall. We began by cleaning the wall, removing loose rocks and replacing them with newer, stronger ones. We also exposed a large portion of the wall that had been buried in the soil. We finished conserving the north side and began conserving the east side using ancient techniques and materials,” he added.
According to Prof. Luca Maria Olivieri, head of the Italian Archaeological Mission, Bazira was one of the most important archaeological sites in Pakistan because it was inhabited from the 6th century BCE to the 14th century CE and contained many archaeological monuments from various civilisations. “The multiphase and diverse history of Bazira city, where we have evidence from the Bronze age until the mediaeval times, makes it one of the most important archaeological sites in Asia,” he said, adding that the massive fortification wall protecting Gwhandai top on the north and east sides was in disrepair.
“The fortification wall with massive bastions was a vital part of the upper part of Baizra, and its preservation was essential.” The wall was originally built during the Indo-Greek period. In the second century CE, the Kushan reshaped it. “It was then repaired during the Hindu Shahi period in the 9th and 10th centuries,” he explained.