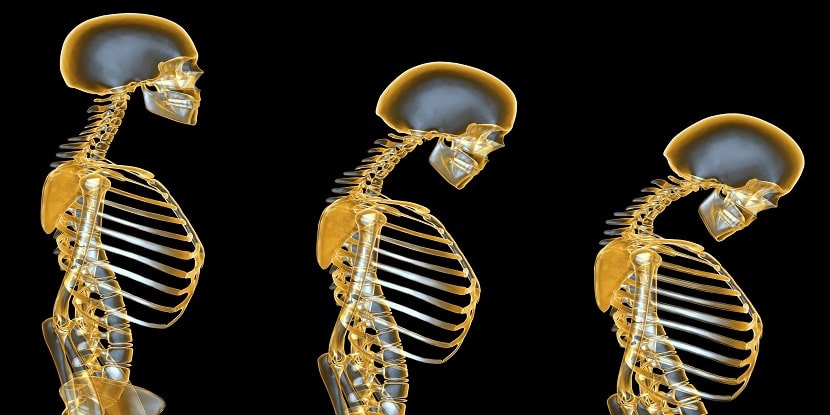
Osteoporosis is a bone issue that builds an individuals’ danger of a break because of a low bone mineral thickness (BMD), disabled bone microarchitecture/mineralization, and additionally diminished bone quality. This asymptomatic condition regularly stays undiscovered until it shows as a low-injury crack of the hip, spine, proximal humerus, pelvis, as well as wrist, which now and again prompts hospitalization.
The pervasiveness of osteoporosis is anticipated to ascend in the United States from around 10 million individuals to more than 14 million individuals by 2020. Although it is ordinarily connected with ladies, it is likewise analyzed in men, who represent an expected one of every five Americans who have osteoporosis or low BMD.
Notwithstanding being the significant reason for breaks in the more established populace, osteoporosis is additionally profoundly connected with individuals getting incapacitated, which can prompt genuine complications.
In 2015, direct clinical costs totaled $637.5 million for deadly fall wounds and $31.3 billion for nonfatal fall wounds. During that year, hospitalizations cost a normal of $30,550 per fall affirmation, totaling $17.8 billion. By 2025, the expense of cracks in the United States is relied upon to surpass $25 billion every year to treat more than 3,000,000 anticipated fractures.
Management of osteoporosis and its related outcomes is important to improve personal satisfaction and diminish monetary weight on the social insurance framework. It will likewise assist with diminishing clinical visits, hospitalizations, and nursing home affirmation.
Lately, significant remedial advances in osteoporosis treatment have been made as researchers increase a more noteworthy comprehension of bone morphology and the basic instruments causing osteoporosis. This article will audit the pathophysiology, etiology, screening, and analysis of osteoporosis; chose proficient rules and suggestions; nonpharmacological the executives; pharmacological alternatives; and the cost-adequacy of those choices.
Foremost osteoporosis is frequently connected with age and sex hormone insufficiency. Age-related osteoporosis results from the consistent weakening of the trabeculae in the bone. Moreover, the decrease of estrogen creation in post-menopausal ladies cause a huge increment in bone misfortune. In men, sex-hormone–restricting globulin inactivates testosterone and estrogen as maturing happens, which may add to the reduction in BMD with time.
Lesser osteoporosis is brought about by a few comorbid ailments or potentially medications.19 Diseases embroiled in osteoporosis frequently include systems identified with the irregularity of calcium, nutrient D, and sex hormones. For instance, Cushing’s disorder has been found to quicken bone misfortune through abundance glucocorticoid creation.
Furthermore, numerous fiery ailments, for example, rheumatoid joint pain, may require the patient to be on long haul glucocorticoid treatment and have been related to optional osteoporosis. Notably, glucocorticoids are viewed as the most widely recognized medicine connected to tranquilize actuated osteoporosis.
BMD has been found to decay quickly in three to a half year of commencement of glucocorticoid therapy. The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) has a point by point suggestions to help in directing treatment determination for the avoidance and treatment of glucocorticoid-prompted osteoporosis (GIO).
The counteraction of osteoporosis should start early and continue entirely through existence with measures that improve or keep up bone wellbeing, including regular physical movement and a fair eating routine, considering not only a sufficient admission of calcium yet in addition to other minerals, proteins, and nourishment rich in antioxidants.
Smoking and liquor misuse ought to have stayed away from. In older persons, who are especially in danger of delicacy fractures, the anticipation of falls and the support of an adequate nutrient D status are fundamental. Appraisal of fracture chance followed by demonstrating effective nonpharmacological and pharmacological management strategies ought to consistently be actualized.
Image source link