There once was a town where all life appeared to live in synchronization with its surroundings. With the chorus of birds, music to the ears and the howling of a wolf in the full moon night. Then an odd blight crept over the area and everything began to change. The once milky streams now filled with murky water. The birds, where had they gone? The wolves never came out of their dens. The hens brooded on the farms, but no chicks hatched.
The trees once laden with fruits now swayed with a whistle of air. In the race between the rabbit and the tortoise, none won. Because, while the rabbit was resting in the forest, a wildfire started on its own and took the rabbit’s life in its sleep. And the tortoise, despite its consistency and steadiness couldn’t reach the finish line and lost the race to the wildfire.
That thirsty crow died of thirst because the pebbles that he threw in the pitcher were actually stones of coal that soaked up whatever water was left in there. This is what the stories for children would look like if climate disaster is not controlled. But the fundamental questions remain that how could humans have created a huge disruption of the environment in such a little time?
How does the climate catastrophe threaten the survival of the entire eco-system, including humans? Is there a way forward to address this global issue? This blog will dwell upon these questions in detail.
There is a scientific consensus on the fact that the Earth is hotter than ever before. And, human actions are primarily responsible for this phenomenon. This poses a direct threat to the survival of human beings living in different parts of the world. It also poses significant economic and geo-political challenges. However, technological innovation, particularly in clean energy, can help solve the crisis. Moreover, better business models and political actions can accelerate this process. Lastly, the urban sprawl in the bustling metropolises needs to be restrained in favor of an eco-friendly urban design. Fortunately, many innovators, companies, states and international bodies are already implementing these solutions.

Causes and Manifestations of Climate Change
In order to assess the impacts and solutions of climate change, it is necessary to explain the causative factors behind it. These are:
Rising Temperatures
The Earth’s average temperature today is about 15 degrees Celsius but it has not always been so. There are natural variations in the climate but scientists say that temperatures are now rising faster than at many other times.
Anthropogenic Causes
The main cause of this rise is anthropogenic, that is, the result of human activity.
Rising Carbon Dioxide Level
Since the Industrial Revolution began in about 1750, Carbon Dioxide levels have risen more than 30%. The accumulation of Carbon Dioxide gas in the atmosphere is higher than at any time in at least 800,000 years. This is due to the fact that industrialization, urbanization and modernization have been fueled by fossil fuels such as coal and oil that release carbon dioxide.
Green House Gases Effect
Additionally, consumption of many animal products releases another pollutant, Methane. These gases cause the heat to trap in the atmosphere, known as the Greenhouse Effect, causing the planet to get warmer.
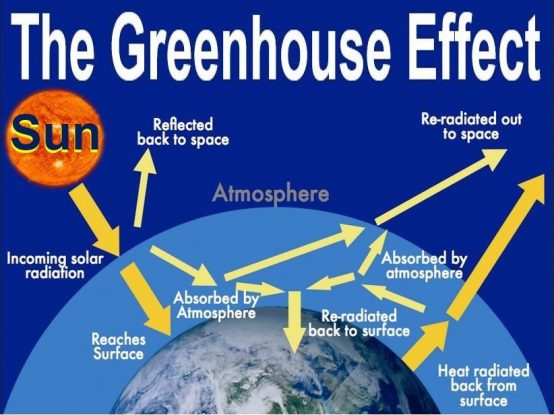
Melting Ice Sheets and Glaciers
The world is at least one degree hotter than pre-industrial times and if it crosses 1.5 degree, the catastrophe would be irreversible. This increase in temperate weather has caused the Arctic Sea ice to melt.
Rising Sea Levels
The warming of oceans has led to rising sea levels on average by 3.1 mm per year.

Changing Weather Patterns
Changing weather patterns have made droughts and heatwaves more frequent. Increase in average humidity has caused massive flooding in many parts of the world.

Extinction of Species
One third of all plant and animal species face the threat of extinction as early as 2070. Hence, climate change threatens the entire eco-system of Earth.
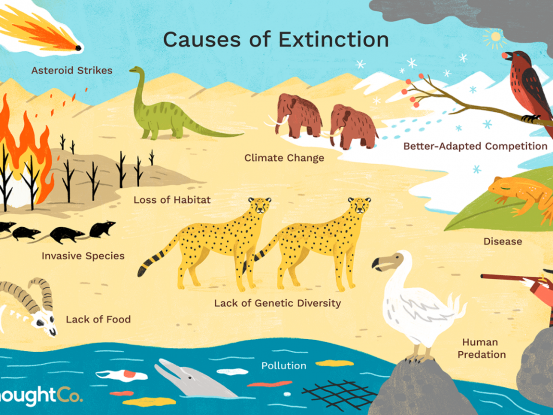
Threats Faced Due To Climate Change Around The World
After looking at the anthropogenic causes of climate change and its various manifestations, this section will explore the ways it tangibly impacts human beings.
Existential Threat Due to Climate Change
The first order of consequence is related to human survival, which has manifested itself in three ways.
First, through rising sea-levels. The 10 largest risk cities which are at a risk due to rising sea-level are mostly in South and Southeast Asia. Back home, The Senate’s Standing Committee on Science and Technology expressed fears in 2015 that Badin, Thatta and Karachi could sink by 2060.
Second, ocean-based storms are getting stronger. Super Typhoon Haiyan was the most powerful tropical cyclone ever recorded. It devastated portions of Southeast Asia, particularly the Philippines, killing at least 6300 people in that country alone.
Third, microbial diseases from the tropics are spreading to the higher latitudes. Changing weather patterns have increased the number of areas where these microbial diseases can become endemic and changed the range of vectors, like mosquitoes and ticks that carry them. Scientists believe that global warming has been already accounted for some 150,000 deaths each year around the world.
This shows the extent to which Climate Change poses a threat to human survival.

Economic Catastrophe Due to Climate Change
First, it has reduced agricultural productivity, especially in low latitude countries. A 2008 study published in Science Journal suggested that, due to climate change, “southern Africa could lose more than 30% of its main crop, maize, by 2030.
In South Asia losses of many local staples, such as rice, millet and maize could top 10%”. In Pakistan, the impact of shortening of Growing Season Length (GSL), heat stress at critical reproductive stages and increased water requirements of crops has caused a decrease in yield in arid and semi-arid areas by about 618%, threatening the food security of the country.
Second, there is an overhang of available fossil fuels in the Carbon reserves owned by Fossil Fuel companies which cannot be burnt. This amount is known as Unburnable Carbon. According to International Energy Agency, out of 28 trillion dollars, only 6 trillion dollars’ worth of reserves are burnable. The rest, 22 trillion dollars, are unburnable.
Thus, the climate crisis is a monumental risk to the global economy.

Geo-Political Impacts of Climate Change
All of the aforementioned issues lead to the third order of consequences which are geo-political in nature.
First, the climate related calamities put a huge burden on administrative and governance apparatuses of States to deal with disaster related emergencies.
Second, as human and economic toll goes up, the cost to manage these crises shoots up as well. These put a huge drain on the already stretched resources of the countries, particularly those in the developing world who also happen to be hardest hit with climate change.
Third, climate-related disasters cause geo-political instability. The historic 2006 drought in Syria destroyed 60 percent of the farms in Syria, killed 80 percent of the livestock, and drove 1.5 million climate refugees into the cities of Syria, where they bumped into another 1.5 million evacuees from the Iraq War.
This, along with other factors, opened the gates of hell that people are trying to close now.
Thus, the administrative, financial and geopolitical burden induced by climate change is enormous.
Solutions to Fight Climate Change
The threats mentioned above are and can be resolved through cutting-edge technological and scientific innovations, in several ways.
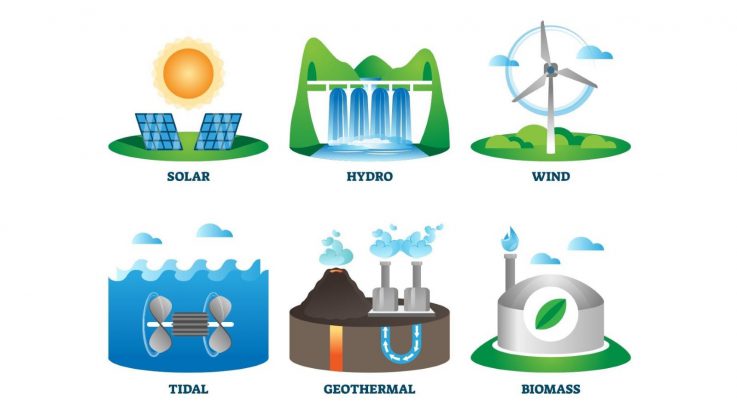
Renewable Energy Resources
First, many countries are now harnessing clean energy through renewable sources i.e. solar, wind and water. For instance, Germany’s 81 percent of all its energy now comes from renewable sources.

Shift Towards E-Vehicles
Second, production of Electric Cars, such as those developed by Tesla, are flooding consumer markets. Their number grew from 0.1 million in 2012 to 3.3 million in 2018.
Recycling and Reusing
Third, recycling and reusing plastic instead of creating it anew from fossil fuels is becoming big business. In January 2020, Vietnam announced that it is creating its first zero plastic waste city.

Reversing Desertification and Deforestation
Fourth, reversing desertification and deforestation through technological tools such as drones. The modern seed-firing drones can plant thousands of trees in a day.

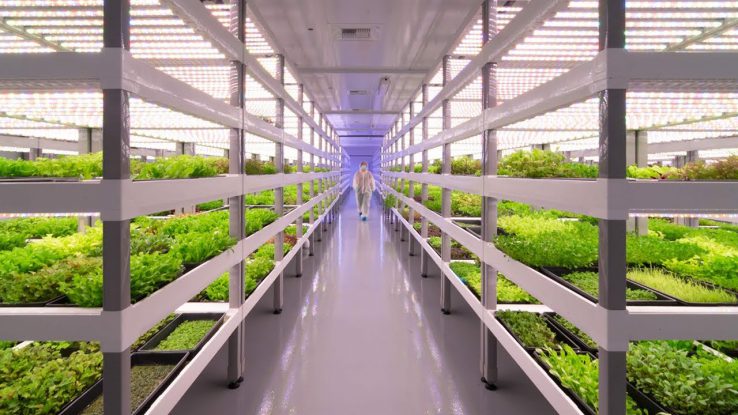
Precision Agriculture And Vertical Farming
Fifth, developing precision agriculture and vertical farming in cities to ensure food security without having to convert forests into agricultural land. Turkey and China are already leading the world in this sector. These innovations show that not only are solutions available but also being employed at a fast pace.

Grid Parity
These innovations are spreading fast because they’ve addressed the elephant in the room: The Grid parity is understood as that threshold, below which renewable electricity is cheaper than electricity from burning fossil fuels. It’s like the difference between zero and one Celsius; the difference between ice and water.
Economically, it’s the difference between markets that are frozen up, and liquid flows of capital into new opportunities for investment. Starting in 2010, investments globally in renewable electricity generation surpassed fossils. Due to this, the 5 trillion-dollar oil and gas industry is facing seismic shift. From 2008 to 2016, the biggest utility company E. ON has seen its share price fall by 75 percent. For renewables, on the other hand, the best projections in 2000 were that by 2010, the world would be able to install 30 gigawatts of wind capacity.
That mark was beaten by 14 and a half times over. In 2002, the best projections were that the world would install one gigawatt per year by 2010. When 2010 came around, that mark was beaten by 17 times over. In 2015, it was beaten 58 times and in 2016 it was beaten a staggering 68 times over. Globally, renewables make up 28 percent of electricity generation.
The exponential increase in investment in renewable sources shows that market-based solutions offer great prospects to tackle climate change.
Climate Change Solutions By Different Countries
China’s Efforts For Climate Change
The above-mentioned achievements are largely attributable to the tremendous strides made by China and some EU countries. China’s renewable power amounted to 40 percent of its total generating capacity, which is greater than the entire power capacity of Japan and India combined. However, one country alone cannot solve this global crisis.
Paris Climate Agreement and US
It is a transnational problem and requires a global political solution. The Paris Agreement was a breakthrough; however, its provisions remain nonbinding. This has to change. Additionally, more and more countries need to regulate carbon footprint on their own. Although President Donald Trump has backed from Paris Agreement, he hasn’t been able to reverse the tide against fossil fuels. Despite partisanship in the U.S Congress, 50 coal power plants have shut since Donald Trump came to office. Since 2010, 289 coal power plants have closed, comprising 40 percent of the US’s coal power capacity.
China and the EU are already cooperating in developing a framework that would provide incentives for greening world trade, primarily through Carbon Tax. Such an agreement would be a breakthrough as these two emitters account for a third of global emissions. If other countries follow suit, governmental regulations and intergovernmental cooperation can prove to be the death knell for unbridled carbon emission.

New Urbanism Movement
While these principles, developed by the New Urbanism Movement, are theoretically very sound, it is pertinent to see whether they are practically and politically viable as well. Fortunately, many countries have already proven that they are.
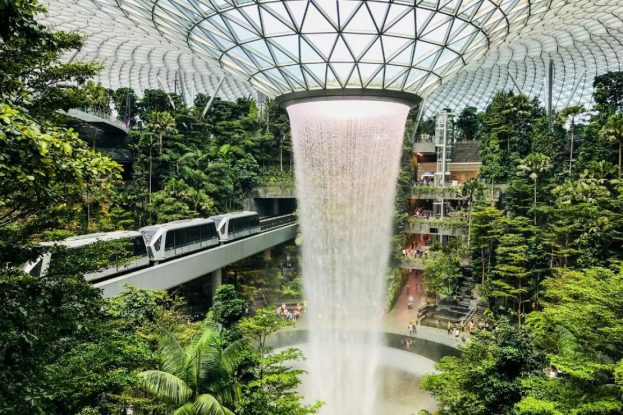
Singapore Biopholic City
Singapore’s biophilic structure, for instance, is putting nature at the heart of its planning and design process. It has issued a landscape replacement policy that ensures any greenery removed through development process to be replaced on the buildings that replace them. In reality, it has tripled the amount of original green footprints through the use of sky gardens.

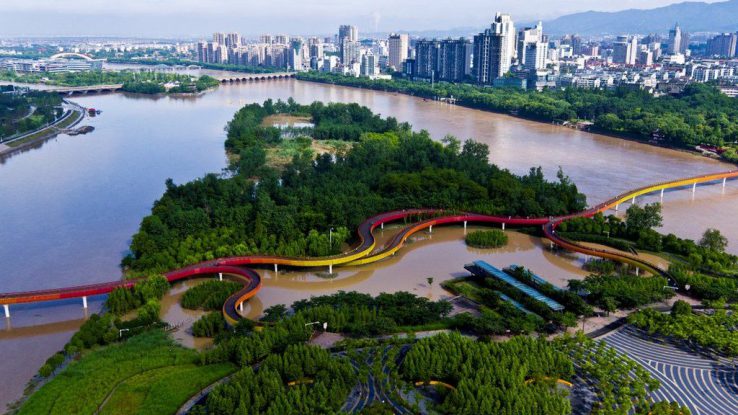
Sponge Cities in China
Similarly, China is building 30 ‘sponge cities’ that can soak up floodwater and prevent disaster. Porous asphalt pavement absorbs the water and retains it, and it can also release the stored water when needed. Hebei City is one of the country’s model sponge cities.

Amsterdam Walkable city
Similarly, Amsterdam has become the bicycle capital of the world. It is equipped with an elaborate network of cycle-paths and lanes, so much so that bikes have become the easiest mode of transport.

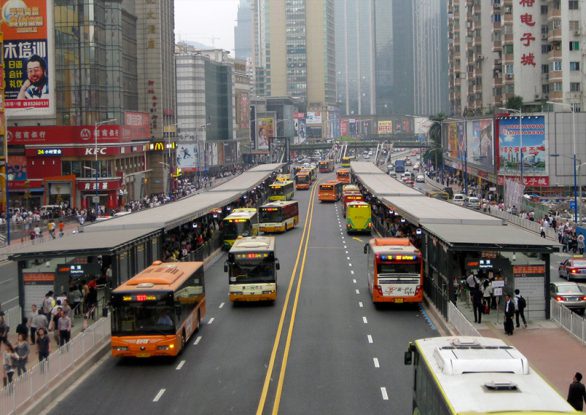
Guangzhou Bus Rapid Transit
In China, the Guangzhou Bus Rapid Transit handles approximately 1,000,000 passenger trips daily, reducing vehicular emission.
Other countries also need to follow suit to systemically eradicate the climate problem.

What Pakistan Can Do To Overcome Climate Catastrophe?
In the light of these challenges and opportunities, Pakistan needs to gear up its efforts to save environment.
Reforestation
First, there is an urgent need for reforestation, using modern tools such as seed firing drones. Campaigns like the Billion-tree Tsunami need to be scaled up.
Proper Waste Management to avoid Glacier Melting
Second, there is a need for waste management strategy for mountainous areas, the lack of which has prompted communities to throw waste in the river or burn it. This leads to black carbon deposition on glaciers that accelerates its melting.
Ban Diesel Engines
Third, diesel vehicles should be banned in mountains as the incomplete burning of the fuel contributes to the rapid melting of glaciers.
Renewable Energy resources
Fourth, there is a need to switch to renewable energy sources. There is a massive potential for solar energy in Thar and hydropower in the North which can provide clean and cost-effective energy.
Construction of Dams
Fifth, developing dams must be constructed to save water and avoid floods.
Conclusion
From the above discussion, it is clear that climate change poses a tangible threat to the collective survival of human beings. These tangible impacts are existential, economic and political in nature. Together, these threats can end or severely limit all forms of human activity by making the planet inhospitable.
From massive flooding to rising sea levels, lower agricultural yields to unburnable carbon, and from mass migration to depletion of resources, climate change impacts all facets of life. In the light of these seemingly insurmountable challenges, the blog has noted various solutions being devised by thinkers, innovators, business leaders and politicians. Notably, technological, economic and political solutions are indeed possible and practicable.
New inventions disrupt the old technologies, better business practices incentivize the growth of these inventions and political regulations accelerate the entire process. Another important aspect is to redesign our urban spaces to make human dwellings more sustainable. Many countries, including China, Turkey, and Germany are already ahead in the game. Others need to catch up. Otherwise, climate change will take everything by storm, quite literally.